Generations of Maintenance
Over a timeline, the expectation of maintenance increases significantly. People understand proper machine maintenance can contribute to production, industry growth & profit.
Initially, maintenance is limited to fixing the problems, Nowadays it’s a part of the business & more proactive.
Let’s go back in time and take a look at maintenance’s history
If we count on history, we can categorize maintenance in 4 generations. Shown in Fig.
Based on Reliability Centred Maintenance, generations were characterized by changes in three areas:
· Expectations of Maintenance
· Views on Equipment Failure
· Maintenance Techniques
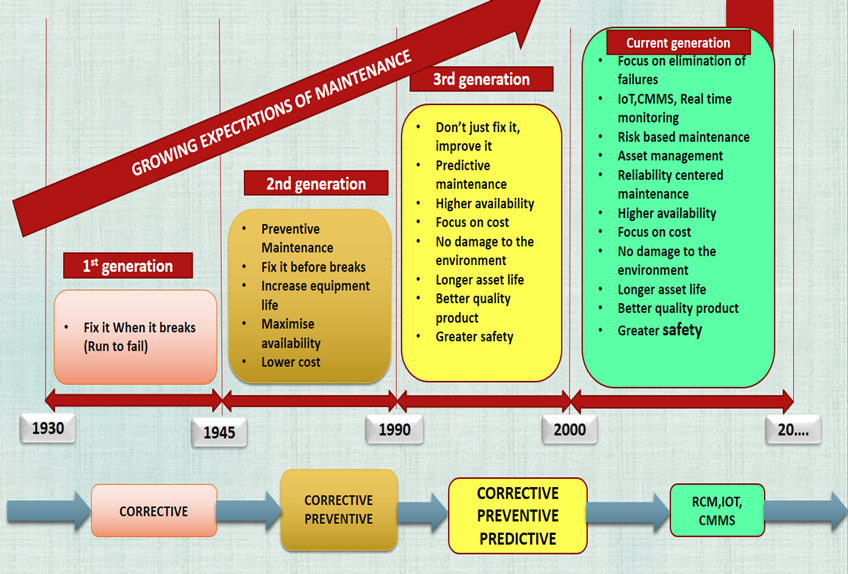
- The First Generation of Maintenance
This is the first generation of maintenance, before land up to the Second World War, could be described in the following terms:
Expectations of Maintenance:
- Fix equipment when it breaks
Views on Equipment Failure:
- All equipment “Wears out”
Maintenance Techniques:
- Fundamental Repair Skills
2. The Second Generation of Maintenance:
After the Second world war, up to the 1990s could be described in the following
Expectations of Maintenance:
- Higher equipment availability
- Longer equipment life
- Lower Maintenance Costs
Views on Equipment Failure:
- Equipment complies with the “Bath-Tub” Curve
Expectations of Maintenance:
- Higher equipment availability & reliability
- Greater safety
- No environmental damage
- Better Product Quality
- Longer Equipment Life
- Greater Cost Effectiveness
Views on Equipment Failure:
- There are 6 failures patterns, following the research of Nowlan and Heap
Maintenance Techniques:
- Condition Monitoring
- Design for Maintainability and Reliability
- Reliability-centered maintenance
- Computer aided maintenance management and information system
- Proactive and strategic thinking
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
